NEOLAiA
“NEOLAiA – Alliance of 8 young European Universities for digital natives, which stands for inclusion, democracy and game-changing.”
The aim of this initiative is to bring together a new generation of creative Europeans able to cooperate across languages, borders and disciplines to address societal challenges and skills shortages faced in Europe. Co-developed by higher education institutions, student organisations, Member States and the Commission, the European Universities Initiative responds to this call. Today, it is one of the flagship initiatives of the EU’s ambitions to build a European Education Area.
“We, as Universities, are the most important drivers of innovation and social change, in our regions, in the EU, and beyond.”

“Zenon is a healthcare-oriented conversational agent”
Zenon conversational agent aims to help doctors caregivers, and patients. Doctors may employ Zenon to handle assessment tasks, extract results from questionnaires and give an overview of the sentiment of the patient. On the other hand, caregivers and patients may use Zenon for frequently asked questions, ask for quick help over an issue, and a report on their progress.

ALAMEDA
“Bridging the Early Diagnosis and Treatment Gap of Brain Diseases via Smart, Connected,
Proactive and Evidence-based Technological Interventions”
ALAMEDA acknowledges that the care of patients with brain disorders is complex and manifestations of certain diseases could worsen over time and seriously impair the quality of life of patients and their caregivers. Through the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) healthcare support systems, the project aims (i) to provide personalized rehabilitation treatment assessments for patients with Parkinson’s, Multiple Sclerosis and Stroke, (ii) to ensure that medical interventions are effective, and (iii) that situations likely to aggravate can be predicted. The success of such applications will provide clinicians with the opportunity to modify interventions based on personalized data recordings, that could include both pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment options. ALAMEDA’s machine learning and AI methodology will ensure that the algorithms are interpretable and provide explanations for their outcomes. Moreover, ALAMEDA will launch a multi-side market information platform, the ALAMEDA Digital Health Innovation Hub, aimed to integrate and make the tools and open-source elements generated by the project available to developers, integrate third-party vendors, and promote the research findings, guidelines, and evaluation results to the broader audience and the relevant decision-makers.

FLOCKAI
An AI-Enabled Framework to Boost Drone Swarm Autonomy
The aim of the FlockAI project is to deliver a framework capable of enabling Machine Learning and its applications to drone technology for handling time-critical missions (e.g., search and rescue missions). Specifically, FlockAI will advance the current research plain by developing innovative AI-enabled self-adaptive algorithms to ease energy consumption and improve data delivery timeliness in drone swarms. To achieve these goals, the FlockAI project will explore the use of various power-efficient machine learning models for dynamically adjusting, in place, the data sensing and routing of data over drone swarms while maintaining mission requirements. The methods delivered by the project will be placed in a modular and reusable framework for drone swarm operation.

EUNOMIA
EUNOMIA is an open-source solution for organizations that would like to deploy their own social media environment with emphasis on trust instead of likes.
EUNOMIA uses a positive-first approach, where the veracity of content is assessed continuously, via user crowdsourcing, over time. In a verifiable way, the origin and path of each bit of content is checked, and information cascade paths are assessed and visualised to the user. Once trust is attached to paths, the content along them are similarly assigned levels of trustworthiness. Citizen participation is actively encouraged in content verification by voting on content trustworthiness. The aim is that the users will take ownership of the problem of disinformation, not to rely on third party fact-checkers or computer software to do it for them. Eunomia offers the means to any social media user to find out who first generated a piece of information; if and how it changed from origin to destination; and how others perceive it.

AI4Media
Europe has a unique, human-centric, and trustworthy ethical brand of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to offer to the world, and a field where such AI is needed and can offer a strong advantage to European actors in the Media.
Motivated by the challenges, risks and opportunities that the wide use of AI brings to media, society and politics, AI4Media aspires to become a centre of excellence and a wide network of researchers across Europe and beyond, with a focus on delivering the next generation of core AI advances to serve the key sector of Media, to make sure that the European values of ethical and trustworthy AI are embedded in future AI deployments, and to reimagine AI as a crucial beneficial enabling technology in the service of Society and Media.
The AI Lab of the University of Nicosia is an Associate Member of the AI4Media project.

DidaXTo
DidaxTo – Learning Patterns for Discovering Domain Oriented Opinion Words
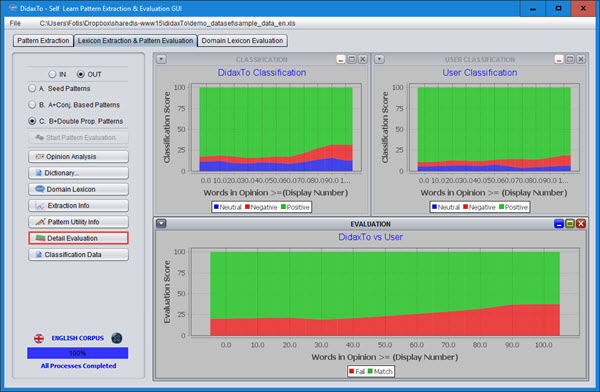
 DidaxTo implements an unsupervised approach for discovering patterns, that will extract a domain-specific dictionary from product reviews. The approach utilizes opinion modifiers, sentiment consistency theories, polarity assignment graphs and pattern similarity metrics. Apart from extracting the dictionary of opinion words, the application allows the evaluation of the dictionary by means of a sentiment classification task on product reviews.
DidaxTo implements an unsupervised approach for discovering patterns, that will extract a domain-specific dictionary from product reviews. The approach utilizes opinion modifiers, sentiment consistency theories, polarity assignment graphs and pattern similarity metrics. Apart from extracting the dictionary of opinion words, the application allows the evaluation of the dictionary by means of a sentiment classification task on product reviews.
The DidaxTo approach is fully presented in the following paper publiced by the Knowledge and Information Systems Journal (KAIS).
![]()
Pantelis Agathangelou, Ioannis Katakis, Ioannis Koutoulakis, Fotios Kokkoras and Dimitrios Gunopulos. “Learning Patterns for Discovering Domain Oriented Opinion Words“, Knowledge and Information Systems Journal (Springer), 55(1), pp.45-77, 2018. DOI: 10.1007/s10115-017-1072-y
DidaxTo (the application) is available for free for non-commercial use. It was developed by Pantelis Agathangelou under the scientific supervision of Ioannis Katakis.
CSRC
CSRC (Cyprus Science and Research Center) will create a Science and Research Centre for promoting innovative research of excellence in Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts and Mathematics (STEAM) Education and in Science Communication. It will aim to enhance everybody’s awareness of scientific and technological endeavours by becoming a unique landmark to be visited by students, educators, entrepreneurs, start-up founders, the wider public and tourists.
CyCAT
The interdisciplinary research center in Cyprus dedicated to Algorithmic Transparency.
The Cyprus Center for Algorithmic Transparency (CyCAT) is an interdisciplinary effort the detection of biases in algorithmic systems as well as the development of more fair and transparent algorithmic processes. We also work with educators and end users in order to promote better awareness of how their interactions feed back into algorithms’ performance/behavior. CyCAT is coordinated by the Open University of Cyprus. The AI Lab at the University of Nicosia is very proud to be a collaborator to this very crucial research task.

